In the world of business, accounting remains paramount, offering a structured approach to track, record, analyze, and relay financial insights. It lays the groundwork for strategic decisions, detailed planning, smart resource use, and assessing a firm’s economic vitality.
Dynamics of Outsourcing vs Offshoring in the Accounting World
As the globe becomes more interconnected through digital evolution, companies are looking beyond their conventional borders. Within this framework, outsourcing accounting and offshoring accounting have risen to prominence. These strategies, representing the core of outsourcing vs offshoring, hold the potential to enhance efficiency, pare down costs, and elevate a firm’s competitive stance.
Such tactics focus on transferring specific tasks or entire functions to external specialists, often situated in varied global regions. Dive further into this narrative for a richer perspective on these evolving accounting strategies.
A. Outsourcing Accounting Services
Outsourcing accounting services refers to the practice of hiring external third-party firms or individuals to handle various accounting functions and tasks that would traditionally be managed in-house. These functions can range from basic bookkeeping and payroll processing to more complex tasks like financial statement preparation, tax compliance, and auditing.
Why Businesses Opt for Outsourcing Accounting Services?

- Cost Savings: Outsourcing accounting can often be more cost-effective than maintaining an in-house accounting department. It eliminates the need for hiring and training full-time staff, providing benefits, and investing in accounting software and infrastructure.
- Expertise: Outsourcing allows businesses to access specialized accounting expertise that they might not have in-house. External firms typically have professionals with diverse skills and experience.
- Focus on Core Activities: By outsourcing non-core functions like accounting, businesses can concentrate their internal resources and efforts on their core activities, which can lead to improved overall performance.
- Scalability: Outsourcing accounting offers scalability, allowing businesses to adjust the level of accounting services they receive based on their current needs. This is particularly beneficial during peak seasons or times of growth.
- Reduced Risk: External firms that specialize in accounting are often more up to date with regulatory changes and compliance requirements, reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
B. Offshoring Accounting Services
Offshoring accounting services involves the relocation of accounting tasks to a different country, often one with lower labor costs, while still maintaining a degree of control and oversight from the home country. Offshoring can be a subset of outsourcing, with the added element of cross-border operations.
Why Businesses Opt for Offshoring Accounting Services?

- Cost Efficiency: Offshoring accounting to countries with lower labor costs can significantly reduce expenses, especially for labor-intensive tasks.
- 24/7 Operations: Time zone differences can be leveraged to achieve continuous work cycles. While one team is finishing work for the day, another in a different time zone can take over, enabling round-the-clock operations.
- Access to Skilled Workforce: Some countries are known for producing highly skilled professionals in fields like accounting. Offshoring allows businesses to tap into these talent pools.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By offshoring accounting non-core activities, businesses can enhance their focus on core competencies, fostering innovation and growth.
- Global Presence: Offshoring can help businesses establish a global presence and adapt to the demands of international markets.
Both outsourcing and offshoring accounting services offer businesses the opportunity to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and access specialized expertise. However, they also come with their own set of challenges, such as cultural differences, communication barriers, and data security concerns, which need to be carefully addressed to ensure successful implementation.
Outsourcing vs Offshoring Accounting: A Direct Comparison
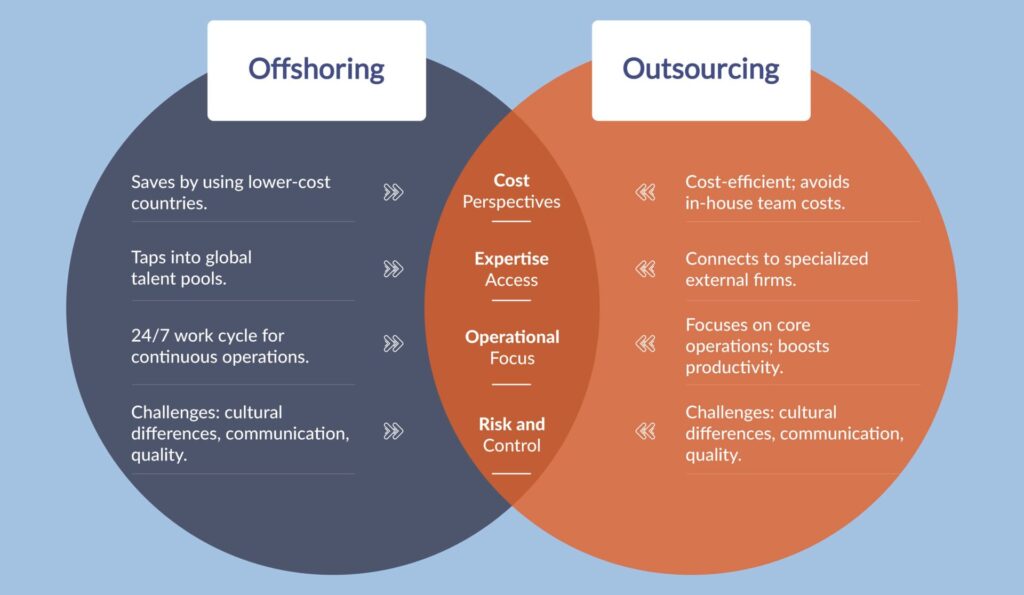
Delving into the world of accounting services, two prevalent strategies emerge: offshoring and outsourcing. While both approaches are designed to optimize business processes, they come with distinct benefits and challenges. Here’s a direct face-off to help you understand the difference:
- Cost Perspectives: While offshoring generally promises significant savings by tapping into lower-cost countries, outsourcing accounting focuses on cost-efficiency by negating the need to hire and train specialized in-house teams.
- Expertise Access: Offshoring gives businesses a chance to tap into global talent pools, drawing from diverse backgrounds to enhance service quality. In contrast, outsourcing connects businesses to external firms with specialized expertise, availing a diverse range of professional skills.
- Operational Focus: Outsourcing allows companies to zero in on their core operations, enhancing their overall productivity. Meanwhile, offshoring, with its 24/7 work cycle due to time zone differences, boosts continuous operations, optimizing efficiency.
- Risk and Control: Businesses that choose to outsource might find a reduced risk linked to compliance, as many external firms stay updated with regulatory shifts. However, this might come at the price of potentially less direct control over processes. Offshoring, while expanding a company’s global presence, might pose challenges related to cultural nuances, communication barriers, and ensuring consistent quality.
In summary, both outsourcing and offshoring offer benefits and challenges, and the choice between them depends on factors such as cost considerations, expertise requirements, risk tolerance, and the desired level of control. Businesses should carefully evaluate these factors before deciding which approach to adopt for their accounting services or other functions.
Comparative Analysis: Outsourcing vs. Offshoring
- Delegation of Functions: Both practices involve delegating specific tasks, functions, or processes to external entities, aiming to improve efficiency and focus on core competencies.
- Cost Efficiency: Both outsourcing and offshoring are often driven by the desire to reduce operational costs and allocate resources more effectively.
- Access to Expertise: Both approaches provide access to specialized expertise that may not be available in-house, whether from domestic or international sources.
- Scalability: Businesses can scale their operations up or down by utilizing external resources through both outsourcing and offshoring.
Major Distinguishing Factors:
- Geographic Focus: The primary distinction lies in the geographic scope. Outsourcing doesn’t inherently involve moving tasks to a different country, whereas offshoring specifically refers to relocating tasks to a foreign location.
- Cost Emphasis: While cost savings are a motivation for both, offshoring places a stronger emphasis on leveraging lower labor costs in a different country.
- Control and Oversight: Offshoring often involves managing teams across different time zones and cultures, which can introduce complexities in terms of control and oversight not as prevalent in outsourcing.
- Global Talent Access: Offshoring is more closely associated with tapping into specific global talent pools, especially in cases where certain countries are known for specialized skills.
Situations Where One May Be Preferred Over the Other
Prefer Outsourcing in case of:
- Local Coordination: When the physical proximity between the home company and the service provider is important for collaboration and coordination, outsourcing within the same country may be preferred.
- Non-Cost Factors: If the primary motivation includes accessing specific expertise, reducing administrative burden, or focusing on core operations, outsourcing could be a suitable choice.
- Less Complex Oversight: When tasks don’t require extensive management of remote teams across time zones and cultures, outsourcing might be simpler to implement.
Prefer Offshoring in case of:
- Cost-Driven Decisions: When significant cost savings are a key objective and the destination country offers lower labor costs, offshoring can result in more substantial savings.
- 24/7 Operations: For businesses aiming to provide continuous services or support to global clients, offshoring can utilize time zone differences for round-the-clock work cycles.
- Specific Skill Needs: When specialized skills are abundant in a specific offshoring destination, it makes sense to leverage those skills through offshoring.
- Scale and Global Presence: Offshoring is well-suited for businesses that need to rapidly scale their operations or establish a global presence by tapping into international talent.
The choice between outsourcing and offshoring depends on various factors including cost considerations, expertise requirements, control preferences, cultural challenges, and the nature of the tasks involved. Each approach has its own benefits and challenges, and businesses should carefully analyze their unique situation before deciding. It’s also worth considering hybrid strategies that combine elements of both outsourcing and offshoring to best meet specific business goals.
In an increasingly interconnected world, businesses are venturing into outsourcing and offshoring more than ever. The pursuit of efficient, cost-effective operations has propelled companies to tap into global talent pools and resources. But the journey isn’t without its challenges. Deloitte’s insightful study delves deep into the nuanced world of outsourcing and offshoring, offering a perspective that goes beyond just cost savings.
· Strategic Alignment
Beyond Cost Savings: Outsourcing and offshoring are not mere cost-cutting tools. They can be strategic drivers when aligned with a company’s long-term vision and objectives.
Bridging Capability Gaps: By tapping into global talent and resources, companies can fill in-house capability voids, introducing fresh perspectives and expertise.
· Risk-Informed Decision Making
Vendor Selection: A balanced approach in choosing vendors, based on capability, compatibility, and cost, can determine the success or failure of an initiative.
Contracts Matter: Detailed and meticulous contracts act as safeguards, clarifying roles, expectations, and liabilities, ensuring smooth collaborations.
Prioritizing Risk Mitigation: Identifying and prioritizing potential risks ensures that companies are prepared to tackle challenges head-on.
· Formal Risk Management Framework
Across the Lifecycle: A risk management framework is essential, not just at the inception but across the entire sourcing lifecycle. It ensures that risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated in real-time.
· Learning and Adapting:
Iterative Learning: The world of outsourcing and offshoring is dynamic. Companies must adopt an iterative approach, learning from past experiences and adapting strategies for future initiatives.
By following the roadmap provided, companies can transform these initiatives from mere operational tactics to strategic, risk-aware successes, driving growth and long-term value.
Conclusion
We explore the realm of accounting service models—Outsourcing vs Offshoring—distinguishing their unique traits and business implications despite their frequent interchangeable use. Through clear definitions, pros & cons, and illustrative examples, we provide businesses with a roadmap to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and goals. Whether you’re a startup or an established enterprise, understanding these models can significantly impact your bottom line and operational efficiency.
Recommendation: Consider Business Size, Goals, and Capacity
- Business Size: Smaller businesses might lean towards local outsourcing, larger ones towards cost-effective offshoring.
- Business Goals: Outsourcing for control and expertise, offshoring for global expansion and cost savings.
- Capacity: Assess ability to manage remote teams, navigate cultures, and coordinate across time zones.
If you enjoyed reading this article, be sure to explore our other blogs on Accounting, Tax, and Outsourcing!
Are you ready to streamline your operations? Benefit from time savings, reduced errors, and expert assistance with AcoBloom’s outsourcing finance and accounting services. Elevate your business with our tailored solutions and unlock efficiency and accuracy in financial strategies. Contact us now to learn more.
