As the world becomes increasingly interconnected and technology-driven, accounting firms, both large and small, are turning to outsourcing to navigate the intricacies of audits and comply with complex financial regulations.
In this blog, we will dive deep into the strategies and tactics essential for maintaining top-notch audit quality in successful outsourcing collaborations within the United States. We will explore a range of approaches and best practices aimed at ensuring the highest levels of audit quality assurance in your outsourcing partnerships. These strategies are designed to help your firm thrive in the dynamic landscape of the accounting industry, where precision, compliance, and excellence are paramount.
Importance of maintaining audit quality in the context of outsourcing

Audit Quality Assurance in the context of outsourcing is of paramount importance for various reasons:
- Compliance with Regulations: Outsourcing accounting services often involve managing sensitive financial information and ensuring compliance with complex regulations such as Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX). High audit quality is necessary to verify that these regulations are adhered to, as non-compliance can lead to severe legal and financial consequences.
- Investor Confidence: High-quality audits provide assurance to investors and stakeholders that a company’s financial statements are accurate and reliable. This confidence can attract investment and support stock prices, contributing to the overall health of financial markets.
- Reputation Management: A company’s reputation is one of its most valuable assets. Maintaining audit quality through outsourcing ensures that financial statements are credible, reducing the risk of scandals or financial irregularities that can damage a company’s reputation and erode trust.
- Fraud Detection: Audits play a crucial role in detecting financial irregularities and fraud. Maintaining audit quality helps identify fraudulent activities early, allowing for corrective action and mitigating financial losses.
- Risk Management: Effective audits are essential for risk management. They provide an independent assessment of a company’s financial health and internal controls, helping to identify potential risks and weaknesses that need to be addressed.
- Data Security: When outsourcing accounting services, sensitive financial data is often shared with external partners. Ensuring data security is vital to protect this information from unauthorized access or breaches that could compromise a company’s financial integrity.
- Auditor Independence: Maintaining auditor independence is critical to the audit process. Clear guidelines and procedures should be in place to prevent conflicts of interest, ensuring that auditors can provide unbiased and objective assessments of a company’s financial statements.
- Continuous Improvement: To ensure audit quality in outsourcing partnerships, regular assessments and feedback mechanisms are essential. These helps identify areas for improvement, refine processes, and maintain or enhance the overall quality of audits over time.
In summary, as outsourcing of accounting services becomes increasingly prevalent, maintaining audit quality remains crucial to uphold regulatory compliance, investor confidence, and a company’s reputation.
Understanding the Significance of Audit Quality Assurance
Audit Quality Assurance (AQA) refers to a set of systematic processes, procedures, and measures designed to ensure that audit engagements are conducted with a high level of quality, integrity, and effectiveness. It encompasses all activities undertaken by audit firms, audit committees, regulators, and other stakeholders to promote and maintain the quality of audits.
The importance of Audit Quality Assurance can be summarized as follows:
- Reliability of Financial Information: AQA ensures that financial statements and related information are audited with a high degree of accuracy and reliability. This is crucial for stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and the public, who rely on audited financial statements to make informed decisions.
- Investor Confidence: AQA helps build and keep investor confidence. When investors trust that audits are conducted rigorously and independently, they are more likely to invest in companies and support financial markets.
- Market Stability: High-quality audits contribute to the stability and credibility of financial markets. They reduce the likelihood of financial scandals and market disruptions that can result from inaccurate financial reporting.
- Protection of Public Interest: AQA is essential for safeguarding public interest. It ensures that auditors adhere to professional standards and ethical principles, protecting the interests of shareholders, employees, and other stakeholders.
Implications of Compromised Audit Quality
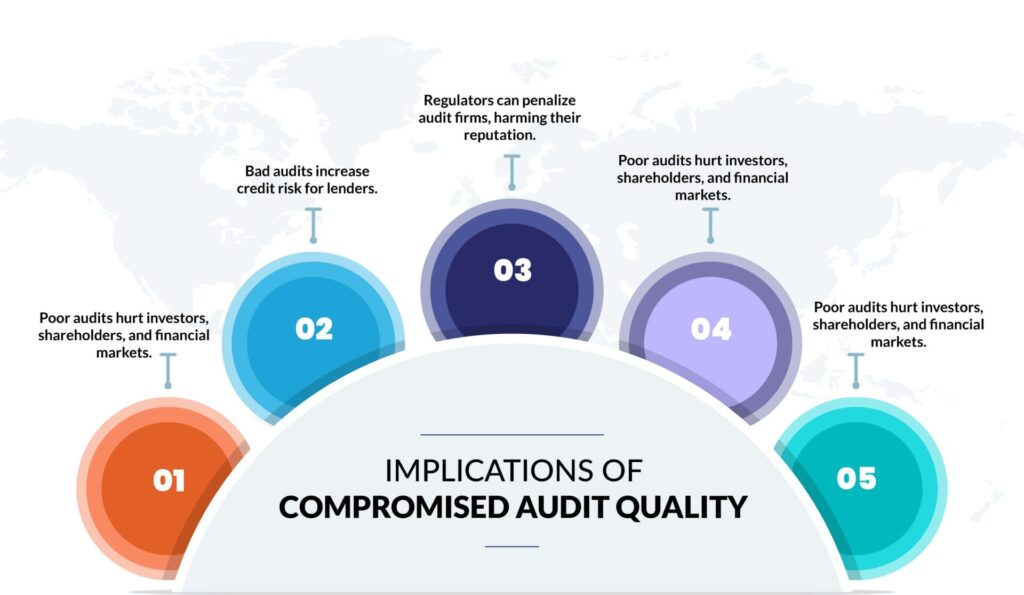
When audit quality is compromised, it can have significant negative implications for various parties and the broader financial ecosystem:
- Investors and Shareholders: Compromised audit quality can mislead investors and shareholders, leading to financial losses, eroded trust, and reduced confidence in financial markets.
- Creditors: Lenders and creditors rely on accurate financial information when extending credit. Poor audit quality can result in increased credit risk and potential defaults.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulators may impose fines and penalties on audit firms or individuals responsible for subpar audits. This can damage the reputation and financial stability of the auditing profession.
- Market Volatility: Financial scandals resulting from compromised audit quality can lead to market volatility, affecting stock prices and overall market stability.
- Legal Consequences: Legal actions, including shareholder lawsuits and regulatory investigations, can arise from audit failures. These legal consequences can be costly for both audit firms and the companies being audited.
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Audits in the U.S.
In the United States, the legal and regulatory framework for audits is primarily governed by the following key elements:
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Enacted in 2002, SOX introduced significant reforms to improve audit quality and corporate governance. It established the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) to oversee and regulate public accounting firms that audit publicly traded companies.
- PCAOB Auditing Standards: The PCAOB develops and issues auditing standards that auditors must follow when conducting audits of public companies. These standards are designed to enhance audit quality, independence, and objectivity.
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): The SEC handles enforcing federal securities laws and overseeing financial reporting by public companies. It has the authority to set reporting requirements and can take enforcement actions against companies and auditors for violations.
- Audit Committees: Public companies must have audit committees composed of independent directors. These committees play a crucial role in overseeing audit quality and the selection and oversight of external auditors.
- Independence Rules: The auditing profession is subject to strict independence rules to prevent conflicts of interest. Auditors must maintain independence from the companies they audit to ensure objectivity.
- Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB): FASB establishes and updates Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the U.S., providing a framework for financial reporting and auditing.
In summary, Audit Quality Assurance (AQA) is vital for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of audits. Compromised audit quality can have serious repercussions for stakeholders and financial markets. The U.S. has established a comprehensive legal and regulatory framework, including SOX, PCAOB standards, SEC oversight, and independence rules, to ensure high-quality audits and protect the public interest.
Challenges in Maintaining Audit Quality Assurance with Outsourcing

Outsourcing accounting services brings forth numerous challenges when it comes to upholding AQA, like:
- Geographic and Time Zone Differences
• Geographic separation can lead to delays in communication and collaboration.
• Time zone differences can hinder real-time interactions between the auditing team and the outsourcing partner, potentially impacting audit progress and responsiveness.
- Cultural and Communication Barriers
• Cultural differences may affect communication styles, leading to misunderstandings or misinterpretations of audit instructions and findings.
• Language barriers can impede effective communication and the ability to convey complex financial and audit concepts accurately.
- Differences in Accounting Standards and Practices
• Outsourcing partners may follow different accounting standards and practices, leading to discrepancies in financial reporting and audit procedures.
• Auditors must navigate these differences and ensure compliance with relevant standards, potentially requiring more training or coordination.
- Reliance on Third-Party Systems and Procedures
• Outsourcing often involves the use of third-party accounting systems and procedures.
• Ensuring the integrity and security of data in these systems is critical to maintaining Audit Quality Assurance, as any flaws or breaches could compromise audit quality.
To address these challenges and maintain Audit Quality Assurance in outsourcing partnerships, organizations must establish clear communication protocols, provide cultural and language training as necessary, and conduct regular assessments to ensure that outsourcing partners adhere to the required accounting standards and security measures. Continuous monitoring and oversight are essential to mitigating these challenges and preserving audit quality.
Best Practices to Ensure Audit Quality Assurance for US Outsourcing Partnerships
1. Selection and Training of Outsourced Partners:
- Conduct thorough due diligence when selecting outsourcing partners, considering their track record and experience.
- Provide regular training sessions and updates on U.S. accounting and audit standards to ensure alignment with your expectations.
2. Clear Communication and Documentation:
- Set clear expectations early in the outsourcing relationship regarding audit scope, objectives, and timelines.
- Maintain consistent and open communication channels to address queries and concerns promptly.
- Emphasize the importance of detailed documentation to ensure transparency and accountability.
3. Use of Technology:
- Leverage cloud-based systems to help real-time collaboration, data sharing, and document management.
- Ensure robust encryption and security measures for data transfer and storage to protect sensitive financial information.
- Implement automated audit tools to enhance accuracy and efficiency in audit procedures.
4. Regular Quality Reviews:
- Establish periodic internal review mechanisms to assess the quality of work performed by outsourcing partners.
- Engage third-party agencies or experts for external reviews to provide unbiased assessments.
- Implement feedback loops to identify and rectify any issues or deficiencies identified during reviews.
5. Customized Outsourcing Agreements:
- Develop outsourcing agreements that clearly define roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
- Specify audit procedures, tools, and methodologies to be used to ensure consistency and alignment with your standards.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) related to quality assurance to track and measure performance.
6. Continuous Training and Professional Development:
- Encourage outsourced teams to acquire U.S.-specific accounting and auditing certifications to enhance their expertise.
- Provide regular updates on changes in regulations, standards, and best practices to keep outsourcing partners informed and compliant.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can establish robust Audit Quality Assurance processes in outsourcing partnerships, ensuring the maintenance of high audit quality standards, compliance with regulations, and the protection of sensitive financial data. This approach promotes transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement in audit quality assurance.
Monitoring and Feedback Mechanisms
Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is essential in outsourced audit services to ensure ongoing audit quality and adherence to established standards. Its significance lies in:
- Quality Assurance: Continuous monitoring helps maintain the quality and integrity of audit services, minimizing the risk of errors, omissions, or compliance issues.
- Risk Mitigation: By regularly assessing outsourced services, organizations can find and address potential risks, reducing the likelihood of financial irregularities or regulatory violations.
- Adaptation to Change: The business environment, regulations, and technologies evolve. Continuous monitoring allows organizations to adapt their audit processes and procedures accordingly.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Proving a commitment to ongoing monitoring and improvement enhances stakeholder confidence in the reliability of audit services and financial reporting.
Techniques to Assess the Quality of Outsourced Audit Services:
Several techniques can be employed to assess the quality of outsourced audit services:
- Quality Reviews: Conduct periodic quality reviews of audit work performed by outsourced partners. These reviews can be internal or external and focus on evaluating the accuracy, completeness, and compliance of audit procedures.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish KPIs related to audit quality, timelines, and client satisfaction. Regularly measure and evaluate these KPIs to assess the performance of outsourcing partners.
- Sampling and Testing: Use sampling and testing methods to independently verify the accuracy of audit work conducted by outsourced teams. This can involve re-auditing selected portions of financial statements or control processes.
- Benchmarking: Compare the performance of outsourcing partners to industry benchmarks and best practices to find areas for improvement.
- Client Surveys: Collect feedback from internal stakeholders and clients who interact with the outsourced audit team. This provides valuable insights into the quality of service, communication, and responsiveness.
Feedback Mechanisms for Continuous Improvement
To drive continuous improvement in outsourced audit services, organizations can implement effective feedback mechanisms:
- Regular Meetings: Schedule regular meetings between the in-house audit team and outsourcing partners to discuss findings, challenges, and improvements.
- Action Plans: Develop action plans based on audit reviews and assessments. Address showed issues promptly and collaboratively.
- Performance Reviews: Conduct periodic performance reviews of outsourcing partners, highlighting strengths and areas needing improvement. Provide constructive feedback to facilitate growth.
- Training and Development: Offer additional training and development opportunities to outsourcing teams to enhance their skills and knowledge.
- Feedback Loops: Set up feedback loops where outsourced partners can share their insights and suggestions for process improvements, fostering a culture of continuous learning.
- Documentation and Reporting: Document all feedback and improvement initiatives. Regularly report on progress to all relevant stakeholders, proving commitment to quality.
By continuously monitoring outsourced audit services, employing assessment techniques, and fostering feedback mechanisms, organizations can not only maintain high audit quality but also drive ongoing improvement, ensuring that audit processes align with changing business needs and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
As outsourcing continues to grow, organizations must adapt to evolving technologies and regulations. The future of outsourcing and Audit Quality Assurance will likely see increased use of AI and automation to enhance audit procedures. The focus will remain on keeping rigorous quality standards and staying ahead of changing accounting and auditing practices.
If you enjoyed reading this blog, be sure to explore our other blogs on Accounting, Audit, and Outsourcing!
Are you considering outsourcing audit services, or do you need assistance in setting up and maintaining Audit Quality Assurance in your outsourcing endeavors? Reach out to us for guidance and support. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of outsourcing while upholding the highest standards of audit quality assurance. Contact us today for expert advice tailored to your needs.
